| Type | Autologous CAR-T | Allogeneic CAR-T |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Uses the patient’s own T-cells | Uses donor T-cells (off-the-shelf) |
| Availability | Requires weeks to modify and expand cells | Readily available, faster treatment |
| Risk of Rejection | Lower risk (cells from self) | Higher risk (cells from donor) |
| Cost | Higher due to personalization | Potentially lower due to mass production |
| Suitability | Best for patients who can wait | Ideal for urgent cases or patients with weak immune systems |
| Procedure | Cells collected from the patient, modified, expanded, and reinfused | Pre-prepared donor cells infused directly into the patient |
| Process | Requires patient-specific T-cell collection, genetic modification, and expansion before infusion | Donor-derived CAR-T cells are pre-manufactured and ready for immediate infusion |
Personalized Treatment : Uses the patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of rejection.
Targeted Action : Specifically designed to attack cancer cells.
Potential for Long-Term Remission : Some patients experience prolonged remission after treatment.
| Category | Type of Car t | Condition or Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Tumors | PSMA | Prostate Cancer, Glioblastoma, Lung Cancer, Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| HER2+ | Breast Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Glioblastoma, Colorectal Cancer, Lung Cancer, Endometrial Cancer, Gall Bladder Cancer, Cholangio Carcinoma | |
| IL-13Rα2 | Glioblastoma, Colorectal Cancer, Breast Cancer, Adreno Corticol Tumor | |
| Claudin 18.2 | Gastric Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatocellularcarcinoma (HCC), Genitourinary Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Esophageal Cancer | |
| GPC3 | Hepatocellularcarcinoma (HCC), Yolk Sac Tumors, Wilms Tumors, Squamous Cell Lung Cancer, Head to Neck Squamous Cell Cancer, Breast Cancer | |
| Mesothelin | Mesothelioma, Pancreatic Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Lung Adenocarcinoma, Cholangiocarcinoma, Gastric Cancer, Triple - Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC), Thymic Cancer, Urothrelial Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Uterine Cancer | |
| CEA | Colorectal Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, Urinary Bladder Cancer, Uterine Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Medullary Thyroid Cancer | |
| CD30 CAR T | Germ Cell Tumor | |
| Blood Cancers | CD19 CAR T | B-ALL & B Cell Lymphoma |
| Dual CD19+CD22 CAR-T | B-ALL & B Cell Lymphoma | |
| BCMA CAR T | Multiple Myeloma | |
| DUAL CS1-BCMA CAR T | Multiple Myeloma | |
| CD30 CAR T | Hodgkin's Lymphoma and ALCL, NK/T-cell lymphoma, PMBCL |
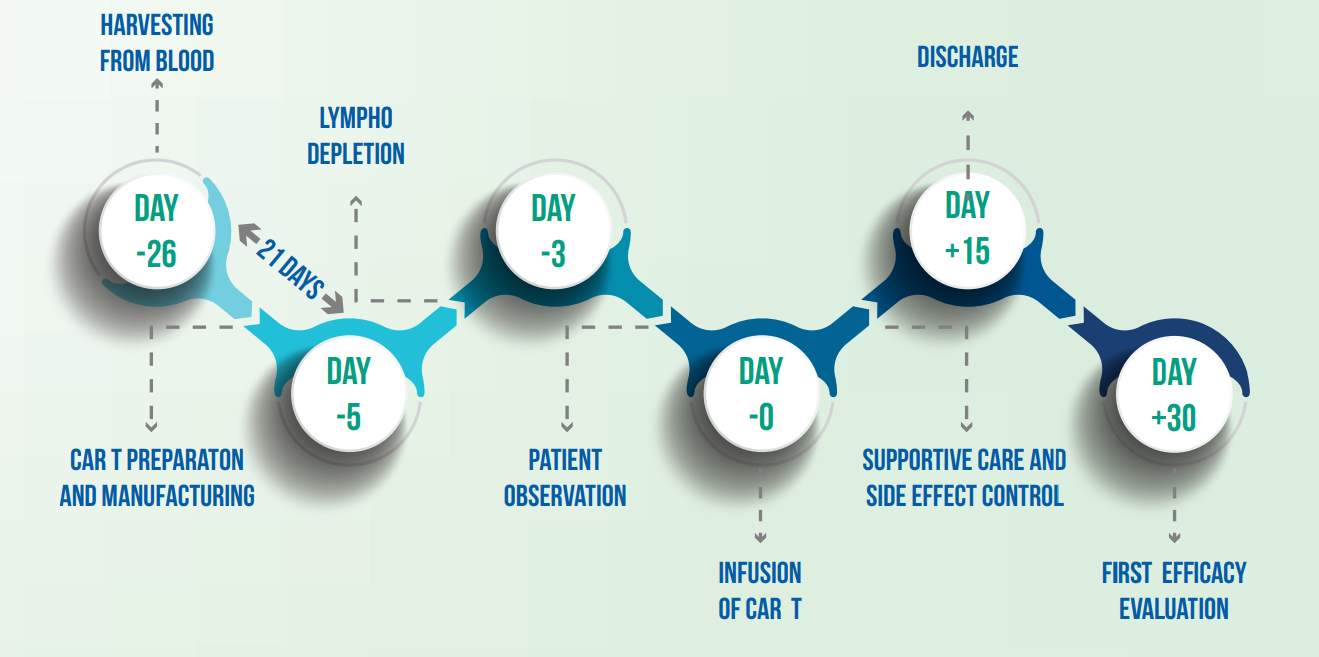
The infusion process is typically done on an inpatient basis.
Regular follow-up is essential to monitor for side-effects and assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Patients may experience fatigue, fever, or other immune-related reactions as the body responds to the therapy.
CAR T-cell therapy is unique because it uses specially engineered immune cells—either from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogenic)—to precisely target and kill cancer cells, unlike conventional treatments that act more broadly.
In a research in 2023, Of the 30 patients, considered to be incurable, 27 (90%) achieved complete remission and 22 showed minimal presence of cancer cells, one month after infusion. Six months post-infusion, the overall survival rate was 78%.
Source: CAR T Cell Therapy: A Versatile Living Drug - PMC
CAR T-cell therapy is for cancer patients whose disease has returned even after trying conventional treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. A thorough evaluation by a medical team is crucial to determine if CAR T therapy is the right option for a patient.
Alternative options may include:
Coverage can vary by insurance provider and plan. Patients should consult their healthcare provider and insurance company to understand their coverage options and potential out-of-pocket costs.
Thane, Khar, Kerala
contact@sunactcancer.com
Phone : +9186553 13412 Toll free : 18002022232